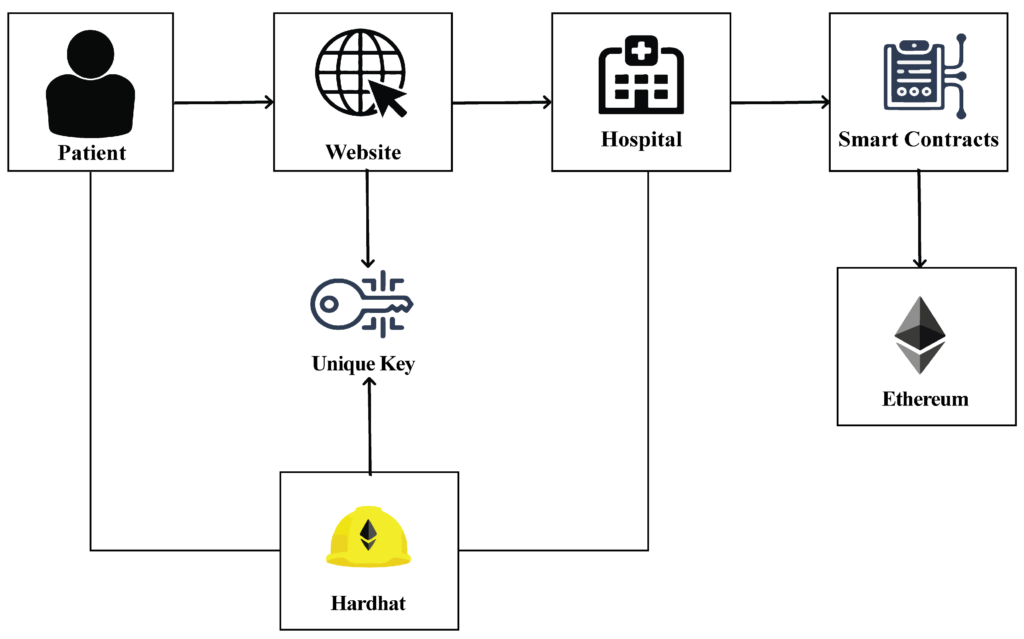
In the digital age, healthcare systems are increasingly shifting from paper-based records to electronic health records (EHRs), which promise to improve patient care, streamline workflows, and facilitate better communication between healthcare providers. However, one of the major challenges that persists in modern healthcare is the lack of interoperability between disparate EHR systems, which can lead to inefficiencies, errors, and delays in patient care. Blockchain technology has the potential to address these challenges by enhancing the interoperability of digital healthcare records, ensuring secure and seamless data sharing across different systems and platforms.
One of the primary barriers to interoperability is the fragmentation of healthcare data. Different healthcare providers, such as hospitals, clinics, and insurance companies, often use different EHR systems that are not designed to work together. As a result, healthcare professionals may have difficulty accessing comprehensive patient data, leading to gaps in patient care. Additionally, the lack of standardized formats for EHRs can make it difficult to share data between different organizations, even if they are using the same type of software. Blockchain can offer a solution by providing a decentralized, standardized framework for storing and sharing health data securely across various platforms.
At its core, blockchain is a distributed ledger technology that records data in an immutable, transparent, and secure manner. Each transaction or piece of data is recorded in a “block” and linked to the previous one, creating a chain of data entries that cannot be altered or tampered with. This makes blockchain particularly well-suited for healthcare, where data integrity and security are paramount. By storing healthcare records on a blockchain, patients and healthcare providers can ensure that the data is tamper-proof, secure, and accessible to authorized parties in real time.
One of the key advantages of using blockchain in healthcare is its ability to enable secure data sharing across different organizations. With blockchain, healthcare data can be stored in a decentralized way, meaning that no single entity has control over the entire dataset. Instead, patient records are stored in multiple nodes across the blockchain network, and access is granted based on predefined permissions. This ensures that patients’ data is only accessible to authorized healthcare providers, such as doctors, hospitals, and specialists, while still allowing for easy sharing of information between different organizations.
For example, when a patient moves to a new city or visits a different healthcare provider, the blockchain can enable the seamless transfer of their health records without the need for physical paperwork or manual data entry. This real-time data sharing can reduce the time spent on administrative tasks, minimize the risk of errors, and ensure that healthcare providers have up-to-date and accurate information when making treatment decisions. Furthermore, blockchain can help avoid duplication of tests, reduce unnecessary procedures, and ultimately lower healthcare costs by ensuring that healthcare providers have access to the most relevant and complete data available.
In addition to enhancing interoperability, blockchain technology can also improve the privacy and security of digital healthcare records. Data breaches and unauthorized access to health information are significant concerns in the healthcare industry, with sensitive patient data being a prime target for cyberattacks. Traditional centralized databases can be vulnerable to hacking, especially when sensitive data is stored in a single location. Blockchain, on the other hand, uses encryption techniques and decentralized storage to ensure that data is secure and resistant to tampering.
Since blockchain records are immutable, any attempts to alter or manipulate a patient’s data would be immediately detectable, providing an added layer of security. Moreover, blockchain allows for the use of advanced cryptographic techniques, such as public and private key encryption, to ensure that only authorized individuals can access or update a patient’s records. Patients can also have more control over their data, as blockchain can enable patients to grant or revoke access to their records, ensuring that they have ownership over their own health information.
Moreover, blockchain can help address challenges related to consent management in healthcare. Consent for data sharing is a critical issue, as patients must be informed and in control of how their health data is used. Blockchain can provide a transparent and auditable record of patient consent, allowing patients to track who has accessed their data and for what purpose. This can help build trust between patients and healthcare providers while ensuring that patient rights are respected.
The integration of blockchain technology into healthcare is still in its early stages, and several obstacles remain, including regulatory hurdles, technical complexities, and the need for industry-wide collaboration. Healthcare organizations will need to work together to establish common standards for blockchain-based EHR systems, and governments must create regulatory frameworks that support the use of blockchain in healthcare. Additionally, healthcare providers will need to invest in the necessary infrastructure and training to implement blockchain solutions effectively.
Despite these challenges, the potential benefits of blockchain for enhancing interoperability in healthcare are significant. By enabling secure, real-time data sharing across different platforms, blockchain can help overcome the fragmentation of healthcare data and ensure that patients receive the best possible care. As the technology continues to evolve and healthcare organizations embrace blockchain solutions, the future of digital healthcare records looks increasingly secure, efficient, and patient-centric.
From Our Editorial Team
Our Editorial team comprises of over 15 highly motivated bunch of individuals, who work tirelessly to get the most sought after curated content for our subscribers.